Renal colic is a common and excruciatingly painful condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It is characterized by sudden, intense pain in the lower back or abdomen, caused by the presence of kidney stones. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis of renal colic is crucial for timely and effective treatment. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of renal colic, exploring its causes, symptoms, and diagnostic procedures. We will also explore the range of treatment options available to provide relief and management for those suffering from renal colic. Additionally, we will discuss lifestyle changes and tips that can help prevent the occurrence of renal colic and reduce the risk of future episodes. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of renal colic, we can empower ourselves and others with knowledge to effectively manage and prevent this debilitating condition.
1. "Understanding Renal Colic: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis"
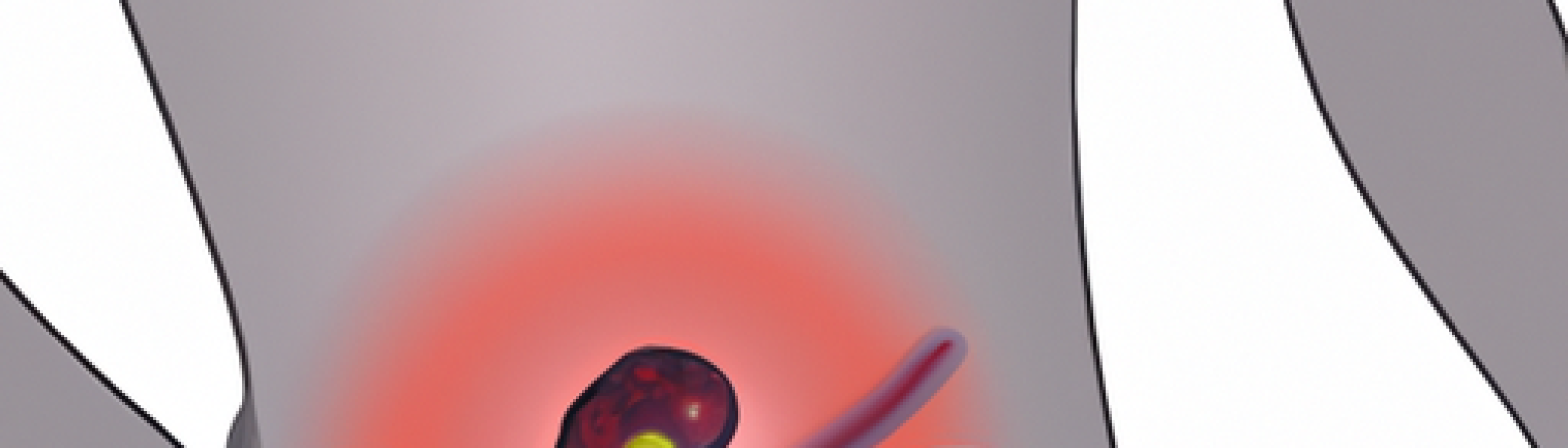
Renal colic is a condition characterized by severe pain in the lower back, side, or groin due to the presence of kidney stones. It is a common urological emergency that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis of renal colic is crucial for timely and effective treatment.
Causes:
Kidney stones, also known as renal calculi, are the leading cause of renal colic. These stones are formed when certain substances in the urine, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid, crystallize and clump together. The size and location of the kidney stone determine the severity of the symptoms. Other factors that contribute to the development of kidney stones include dehydration, certain medical conditions like hyperparathyroidism, and a family history of kidney stones.
Symptoms:
The hallmark symptom of renal colic is excruciating pain, often described as one of the most severe pain experiences a person can have. The pain typically starts suddenly and may radiate from the back to the abdomen, groin, or genitals. Patients may also experience blood in the urine (hematuria), frequent urination, urgency to urinate, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, and nausea or vomiting. The intensity of the pain can fluctuate as the stone moves within the urinary tract.
Diagnosis:
Prompt and accurate diagnosis of renal colic is essential to alleviate pain and prevent complications. Healthcare professionals rely on various diagnostic methods to identify kidney stones and determine the most appropriate treatment. These include:
1. Medical history and physical examination: The doctor will inquire about the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and family history of kidney stones. A thorough physical examination may reveal tenderness in the affected area.
2. Imaging tests: Imaging techniques like ultrasound, X-ray, and computed tomography (CT) scans are commonly used to visualize the urinary tract and identify the presence, size, and location of kidney stones. CT scans are particularly effective in detecting even small stones and providing detailed information about their composition.
3. Urine analysis: A urine sample may be collected and analyzed to check for the presence of blood, infection, or crystals. This can help confirm the diagnosis and guide further treatment.
4. Blood tests: Blood tests may be conducted to assess kidney function, measure levels of certain substances like calcium and uric acid, and identify any underlying conditions that may contribute to stone formation.
In conclusion, renal colic is a painful condition caused by kidney stones. Recognizing the causes, symptoms, and accurate diagnosis of renal colic is crucial for effective management. Prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment can help alleviate pain, facilitate
2. "Effective Treatment Options for Renal Colic: Relief and Management"
Renal colic, a condition characterized by sudden and severe pain in the lower back or side, is often caused by the presence of kidney stones. The excruciating pain associated with renal colic requires immediate medical attention and effective treatment options to alleviate discomfort and manage the underlying causes.
One of the primary goals in treating renal colic is to relieve pain. Depending on the severity of the pain, over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen sodium may be recommended. These medications work by reducing inflammation and providing pain relief. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any medication, as they will assess the patient’s medical history and determine the appropriate dosage.
For more severe cases of renal colic, stronger pain medications may be prescribed, such as opioids. These medications are highly effective in providing immediate pain relief, but they are typically used for short periods due to their potential for addiction and other side effects.
In addition to pain relief, treatment for renal colic focuses on managing the underlying causes, primarily kidney stones. Small kidney stones may pass through the urinary system naturally, but larger stones may require intervention. One effective treatment option for larger stones is extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL). During this procedure, shock waves are used to break the stones into smaller pieces, making them easier to pass or remove.
Another option for treating kidney stones is ureteroscopy. This minimally invasive procedure involves passing a thin tube with a camera through the urinary tract to locate and remove the stones. Ureteroscopy is particularly useful for stones located in the lower part of the urinary tract.
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary, especially if the stones are too large or causing severe complications. Surgical procedures like percutaneous nephrolithotomy involve making a small incision in the back to access and remove the stones.
Prevention is another vital aspect of managing renal colic. Patients who have experienced renal colic due to kidney stones are often advised to make dietary and lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of recurrence. Increasing fluid intake, particularly water, helps in flushing out minerals and preventing the formation of stones. Additionally, reducing the consumption of oxalate-rich foods, such as spinach and chocolate, and limiting salt intake can also be beneficial.
In conclusion, effective treatment options for renal colic aim to provide pain relief and manage the underlying causes, primarily kidney stones. Pain medications, such as NSAIDs and opioids, can help alleviate the excruciating pain associated with renal colic. Procedures like ESWL and ureter
3. "Preventing Renal Colic: Lifestyle Changes and Tips to Reduce the Risk"
Preventing Renal Colic: Lifestyle Changes and Tips to Reduce the Risk
While renal colic can be a painful and distressing condition, there are certain lifestyle changes and preventive measures that can help reduce the risk of its occurrence. By adopting a few healthy habits, individuals may be able to mitigate the chances of developing renal colic and improve their overall kidney health. Here are some tips and recommendations to consider:
1. Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is crucial for maintaining optimal kidney function. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps to flush out toxins and prevent the build-up of mineral deposits in the kidneys, which can lead to the formation of kidney stones. Aim to consume at least eight glasses of water daily, or more if you are physically active or live in a hot climate.
2. Follow a Balanced Diet: A well-balanced diet plays a vital role in promoting kidney health. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your meals. Limit your intake of processed foods, sodium, and refined sugars, as these can contribute to kidney stone formation. Additionally, reducing the consumption of oxalate-rich foods such as spinach, rhubarb, and chocolate may also help prevent the formation of certain types of kidney stones.
3. Watch Your Salt Intake: Excessive sodium intake can increase the risk of kidney stone formation. Avoid adding extra salt to your meals and minimize the consumption of processed and packaged foods, as they are often high in sodium content. Instead, opt for natural herbs and spices to enhance the flavor of your dishes.
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a risk factor for kidney stones and renal colic. Aim to maintain a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet. Losing excess weight can help reduce the strain on the kidneys and lower the chances of developing kidney stones.
5. Limit Alcohol and Caffeine Consumption: Both alcohol and caffeine can dehydrate the body, which can contribute to the formation of kidney stones. Limit your intake of alcoholic beverages and caffeinated drinks like coffee, tea, and soda. Instead, opt for healthier alternatives like herbal teas and infused water.
6. Quit Smoking: Smoking is detrimental to overall health, including kidney function. It can increase the risk of kidney stones and other kidney-related diseases. Quitting smoking not only reduces the risk of renal colic but also improves overall health and wellbeing.
7. Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also promotes good kidney function. Exercise improves blood circulation, which aids in the removal of waste products from the body. Consult with your healthcare professional before starting